Polysomnography: The Complete Guide to Sleep Studies in 2026
Everything you need to know about the gold-standard overnight sleep study - from what polysomnography measures to understanding your results, costs, and treatment options after diagnosis.
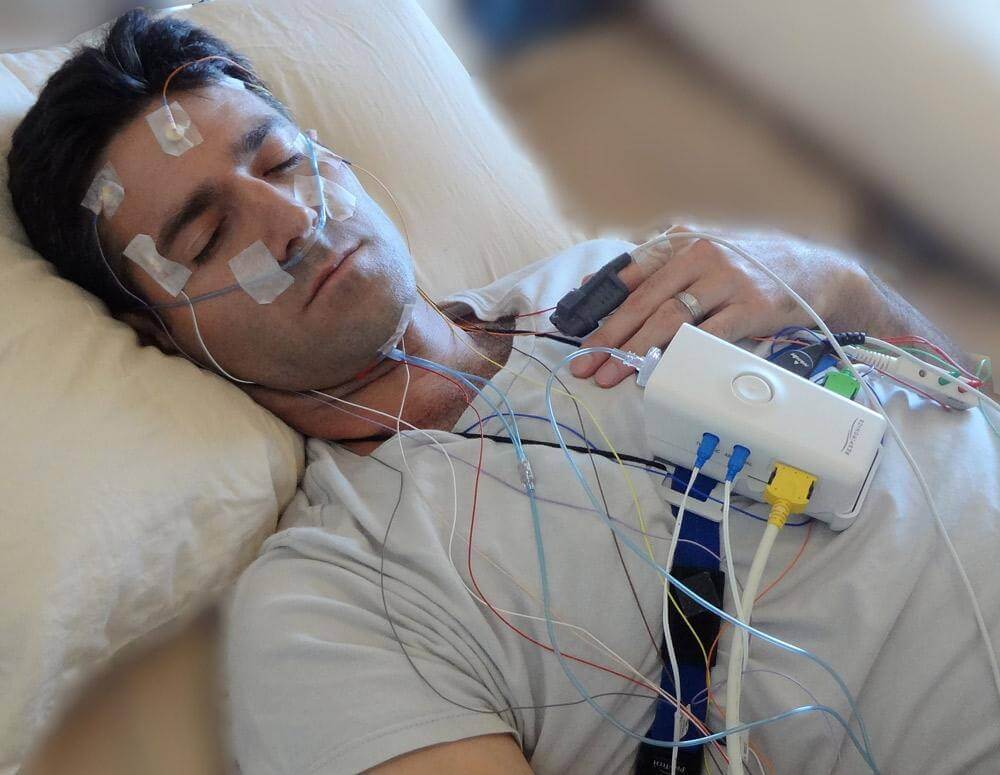
Polysomnography (PSG) is the gold-standard diagnostic test for sleep disorders, providing comprehensive overnight monitoring of brain activity, breathing patterns, heart rate, oxygen levels, and body movements. According to the Sleep Foundation, if you're experiencing chronic fatigue, loud snoring, witnessed breathing pauses, or excessive daytime sleepiness, a sleep study can reveal the underlying cause and guide effective treatment. With over 22 million Americans affected by sleep apnea according to NIH research and 80% of cases remaining undiagnosed, understanding polysomnography is the first step toward reclaiming restful, restorative sleep. For those diagnosed with mild-to-moderate sleep apnea, innovative solutions like the Back2Sleep intranasal orthosis offer an effective alternative to traditional CPAP therapy.
This comprehensive guide covers what happens during a polysomnography exam, who needs one, how to prepare, what results mean, costs and insurance coverage, and the latest 2026 innovations in sleep monitoring technology including AI-powered analysis and at-home options.
Polysomnography Quick Facts: Everything at a Glance
| Key Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What does polysomnography diagnose? | Sleep apnea (obstructive, central, mixed), narcolepsy, restless legs syndrome, periodic limb movement disorder, REM behavior disorder, insomnia, parasomnias, and circadian rhythm disorders |
| What does a polysomnogram measure? | Brain waves (EEG), eye movements (EOG), muscle activity (EMG), heart rhythm (ECG), breathing effort, airflow, oxygen saturation (SpO2), body position, and snoring sounds |
| How much does a polysomnography cost? | $500-$3,000 without insurance; typically $100-$500 with insurance after deductible; Medicare covers 80% of approved amount |
| Is polysomnography covered by insurance? | Yes - most insurance plans cover PSG when medically necessary with physician referral; pre-authorization often required |
| How long does a sleep study take? | Overnight (approximately 7-9 hours of recording); arrive 1-2 hours early for setup; depart by 7-8 AM |
| What is the difference between PSG and HSAT? | PSG (in-lab) measures brain waves + comprehensive parameters with technician; HSAT (home) measures breathing/oxygen only without EEG or supervision |
| How long to get polysomnography results? | 1-2 weeks for full analysis and report; follow-up appointment scheduled to discuss findings and treatment |
| Is polysomnography painful? | No - completely non-invasive; involves only external sensors attached with paste/tape; no needles or internal procedures |
Sleep Disorders: The Numbers You Need to Know
What is Polysomnography? Understanding the Gold-Standard Sleep Study
Polysomnography, commonly called a sleep study or PSG test, is a comprehensive overnight examination that records multiple physiological parameters while you sleep. The term comes from Greek: "poly" (many), "somnus" (sleep), and "graphein" (to record). According to the Mayo Clinic, unlike simple screening tools, polysomnography provides objective, quantitative data that reveals exactly what happens during each stage of your sleep cycle.
What Does a Polysomnogram Measure? Complete Parameter List
Electroencephalogram (EEG) - Brain Waves: Multiple electrodes on the scalp record electrical brain activity, identifying sleep stages (N1, N2, N3 deep sleep, REM) and detecting micro-arousals that fragment sleep without your awareness.
Electro-oculogram (EOG) - Eye Movements: Sensors near the eyes track eye movement patterns that distinguish REM sleep (when eyes move rapidly) from non-REM stages - essential for diagnosing narcolepsy and REM behavior disorder.
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) - Heart Rhythm: Chest electrodes continuously monitor heart rate and rhythm, detecting arrhythmias, bradycardia (slow heart rate), or tachycardia (fast heart rate) associated with breathing events.
Respiratory Monitoring - Breathing Patterns: Nasal cannula and thermistor measure airflow; chest and abdominal belts detect respiratory effort, distinguishing obstructive apneas (blocked airway with effort) from central apneas (no effort).
Electromyogram (EMG) - Muscle Activity: Sensors on chin monitor muscle tone (decreases in REM), while leg sensors detect periodic limb movements and restless legs syndrome episodes.
Pulse Oximetry - Oxygen Saturation: Fingertip sensor continuously measures blood oxygen levels (SpO2), revealing desaturations during apneas - critical for assessing severity and cardiovascular risk.
Position Sensor - Body Position: Tracks whether you're sleeping supine (back), lateral (side), or prone (stomach) - many patients have position-dependent apnea that worsens on their back.
Audio Recording - Snoring Sounds: Microphone captures snoring intensity, frequency, and correlation with respiratory events to characterize upper airway obstruction patterns.
Conditions Diagnosed by Polysomnography
Sleep Disorders Identified Through PSG:
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Repeated upper airway collapse causing breathing cessation - the most common indication for sleep studies
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): Brain fails to send proper signals to breathing muscles, causing breathing pauses without obstruction
Complex/Treatment-Emergent Sleep Apnea: Combination of obstructive and central events, often appearing during CPAP therapy
Narcolepsy: Abnormal REM sleep intrusion causing excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) / PLMD: Uncomfortable leg sensations causing movement urges and periodic limb movements during sleep
REM Behavior Disorder: Loss of normal REM muscle paralysis causing patients to physically act out dreams
Parasomnias: Sleepwalking, night terrors, confusional arousals, sleep eating disorders
Circadian Rhythm Disorders: Delayed/advanced sleep phase syndrome, shift work disorder, jet lag disorder
Insomnia: Objective documentation of sleep latency, efficiency, and architecture when subjective reports need verification

Polysomnography vs Home Sleep Test: Which Do You Need?
Understanding the difference between PSG and home sleep apnea testing (HSAT) helps you know what to expect and ensures you receive the appropriate test for your situation. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) provides comprehensive guidelines on when each test is appropriate.
| Feature | Polysomnography (PSG) | Home Sleep Apnea Test (HSAT) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Accredited sleep laboratory | Your own home/bed |
| Parameters Measured | EEG, EOG, EMG, ECG, breathing, SpO2, position, video (10+ channels) | Breathing, SpO2, heart rate, position (4-7 channels) |
| Sleep Staging | Yes - complete sleep architecture analysis | No - estimates total sleep time |
| Technician Supervision | Yes - continuous overnight monitoring | No - self-administered |
| Cost | $1,500-$3,000 (facility); $500-$1,500 after insurance | $150-$500 (device); $50-$200 after insurance |
| Wait Time | Often weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Failure Rate | Less than 5% | 15-20% (sensor displacement, insufficient data) |
| Best For | Complex cases, suspected non-apnea disorders, comorbidities | High OSA probability, no significant comorbidities |
| Diagnoses | All sleep disorders | Obstructive sleep apnea only |
When Polysomnography is Required (HSAT Not Appropriate):
- Suspected central sleep apnea, narcolepsy, parasomnia, or seizure disorder
- Significant cardiac disease, heart failure, or severe COPD
- Neuromuscular disease affecting breathing
- History of stroke with suspected sleep-disordered breathing
- Failed or inconclusive home sleep test
- Need for CPAP titration in complex cases
- Pediatric patients (children under 18)
2026 Innovations in Sleep Monitoring Technology
Sleep medicine has evolved rapidly with new technologies making diagnosis more accessible and accurate. Here are the latest advances transforming polysomnography:
AI-Powered Sleep Analysis
SleepFM and similar AI models now analyze sleep data with 90%+ accuracy, automatically detecting apneas, sleep stages, and micro-arousals - reducing analysis time from hours to minutes while improving consistency.
Patch-Based Home PSG
Devices like Onera hPSG offer full polysomnography at home using disposable sensor patches - measuring EEG, EOG, EMG, and all traditional parameters without wires or sleep lab visits.
Wearable Sleep Trackers
FDA-cleared wearables like Withings Sleep Analyzer provide clinical-grade apnea detection from under-mattress sensors, offering screening-level accuracy for at-risk populations.
Telemedicine Integration
Remote sleep consultations with board-certified specialists have become standard, allowing diagnosis and treatment initiation without in-person visits - especially valuable for rural areas.

What Happens During a Polysomnography? Step-by-Step Guide
How to Prepare for a Sleep Study
Pre-Study Instructions (Critical for Accurate Results):
- Avoid caffeine after 2 PM on study day - no coffee, tea, energy drinks, chocolate, or sodas
- No alcohol for 24 hours before testing - alcohol suppresses REM and worsens apnea
- Skip daytime naps to ensure adequate sleep pressure at bedtime
- Wash hair but avoid products - no oils, gels, hairspray, or conditioners that interfere with electrode adhesion
- Remove nail polish from at least one finger for pulse oximeter accuracy
- Continue regular medications unless your doctor specifically instructs otherwise
- Bring comfortable two-piece pajamas (not one-piece) to accommodate chest sensors
- Pack toiletries and your own pillow if desired for comfort
The Polysomnography Procedure: What to Expect
Evening Arrival
Arrive at sleep lab 1-2 hours before your normal bedtime (typically 8-9 PM). Complete paperwork and change into sleepwear.
Sensor Placement
Technician applies electrodes to scalp, face, chest, and legs using conductive paste and tape - takes 30-45 minutes. Process is painless.
Calibration Tests
Brief "biocalibration" where you follow commands (look left, right, blink, hold breath) to verify all sensors are working properly.
Overnight Recording
Sleep naturally while technician monitors from adjacent room. Can request bathroom breaks via intercom. Recording continues 6-8 hours.
Morning Departure
Awakened around 6 AM, sensors removed, adhesive cleaned off. Shower available at most facilities. Depart by 7-8 AM.
Results Analysis
Sleep specialist analyzes data over 1-2 weeks. Follow-up appointment scheduled to discuss findings, diagnosis, and treatment plan.
Most patients report sleeping somewhat less than normal due to the unfamiliar environment and sensors, but typically achieve enough sleep (minimum 4-6 hours) for diagnostic purposes. Don't worry if you don't sleep perfectly - the study can still provide valuable data.
Understanding Your Polysomnography Results
Key Metrics in Your Sleep Study Report
| Metric | What It Measures | Normal vs. Abnormal |
|---|---|---|
| Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) | Number of apneas + hypopneas per hour of sleep | Normal: <5 | Mild OSA: 5-14 | Moderate: 15-29 | Severe: 30+ |
| Oxygen Desaturation Index (ODI) | Number of times SpO2 drops 3-4% per hour | Normal: <5 | Higher ODI = greater cardiovascular risk |
| Minimum SpO2 | Lowest oxygen saturation during sleep | Normal: >90% | <85% concerning | <80% severe |
| Sleep Efficiency | Percentage of time in bed actually asleep | Normal: >85% | <80% indicates sleep fragmentation |
| Sleep Latency | Time to fall asleep after lights out | Normal: 10-20 minutes | <8 min suggests sleep deprivation |
| REM Latency | Time to first REM period | Normal: 90-120 minutes | <15 min suggests narcolepsy |
| Arousal Index | Brief awakenings per hour | Normal: <10/hour | Elevated indicates fragmented sleep |
| PLMI (Periodic Limb Movement Index) | Leg movements per hour | Normal: <15/hour | >15 with arousals = PLMD diagnosis |
Can You Fail a Sleep Study?
A common concern: "Can you fail a sleep study?" The answer is no - there's no pass/fail. A sleep study simply documents what happens while you sleep. Even if you feel you slept poorly, the data usually provides enough information for diagnosis. The study can be considered "inconclusive" if:
- Total sleep time was less than 2-4 hours (insufficient data)
- Sensors repeatedly fell off during the night
- Technical equipment failure occurred
- Results are borderline and clinical picture remains unclear
In these cases, your doctor may recommend repeating the study or proceeding with treatment based on clinical assessment.

Polysomnography Cost: With and Without Insurance
How Much Does a Sleep Study Cost?
| Type of Sleep Study | Without Insurance | With Insurance (typical) |
|---|---|---|
| In-Lab Polysomnography (PSG) | $1,500 - $3,500 | $100 - $500 after deductible |
| Split-Night Study (Diagnosis + CPAP) | $2,000 - $4,000 | $150 - $600 after deductible |
| CPAP Titration Study | $1,500 - $3,000 | $100 - $400 after deductible |
| Home Sleep Apnea Test (HSAT) | $150 - $500 | $0 - $150 after deductible |
| Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) | $1,000 - $2,000 | $100 - $300 after deductible |
Is Polysomnography Covered by Insurance?
Yes, most insurance plans cover polysomnography when medically necessary. Coverage requirements typically include:
Insurance Coverage Requirements:
- Physician referral/prescription documenting medical necessity
- Pre-authorization from insurance company (required by many plans)
- Accredited sleep facility meeting AASM or state standards
- Appropriate diagnosis codes (ICD-10) on claim forms
- Medicare: Covers 80% of approved amount for PSG (CPT 95810) with 20% patient responsibility
- Medicaid: Coverage varies by state - check your specific plan
Pro tip: If cost is a concern, ask your doctor about home sleep apnea testing first - it's significantly cheaper and often sufficient for straightforward OSA cases. In-lab PSG can follow if home test results are inconclusive or you need evaluation for non-apnea disorders.
After Polysomnography: Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
If your polysomnography confirms sleep apnea, several treatment options are available depending on severity and your preferences:
CPAP Therapy
Gold standard for moderate-severe OSA. Continuous positive airway pressure delivered via mask keeps airways open. Highly effective but 40-50% of patients abandon within first year due to discomfort.
Oral Appliances
Mandibular advancement devices reposition jaw forward to prevent airway collapse. Custom-fitted by dentist. Best for mild-moderate OSA or CPAP-intolerant patients.
Back2Sleep Orthosis
Innovative intranasal device that maintains airway patency from within. No mask, no machine, no noise. 92% effectiveness for mild-moderate OSA. Works from first night.
Lifestyle Modifications
Weight loss, positional therapy, avoiding alcohol before bed. Weight loss of 10-15% can reduce AHI by 50% in overweight patients. Often combined with other treatments.
Why Choose Back2Sleep After Polysomnography?
For patients diagnosed with mild-to-moderate sleep apnea who struggle with CPAP compliance, the Back2Sleep intranasal orthosis offers a compelling alternative:
- No mask, hose, or machine - complete freedom during sleep
- Immediate results - works from the first night without adaptation
- 92% user satisfaction compared to 40-60% CPAP adherence rates
- Travel-friendly - no electricity, portable anywhere
- Cost-effective - one-time purchase vs. ongoing CPAP supplies
Frequently Asked Questions About Polysomnography

Take the First Step Toward Better Sleep
Polysomnography is the gold-standard diagnostic tool that transforms vague symptoms like fatigue, snoring, and poor sleep into actionable diagnoses with targeted treatments. With 936 million people worldwide affected by sleep-disordered breathing and 80% undiagnosed, getting tested could be the most important health decision you make.
If your polysomnography confirms mild-to-moderate obstructive sleep apnea, consider the Back2Sleep intranasal orthosis as an effective, comfortable alternative to CPAP - 92% user satisfaction and immediate relief from night one.
Explore our sleep health blog for the latest research and practical tips, or contact our specialists for personalized guidance on your sleep health journey.