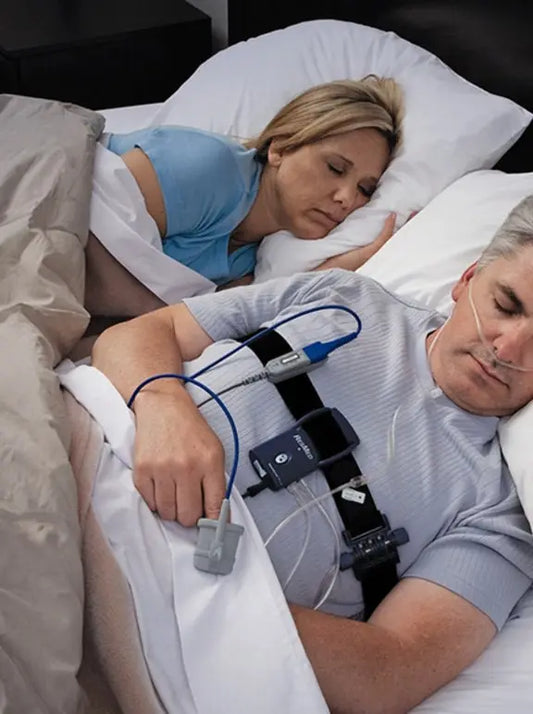
Snoring can turn a night's rest into a real struggle, not only for the snorer but also for those around him or her.
This phenomenon, often perceived as a simple inconvenience, may in fact signal underlying health problems such as sleep apnea.
Fortunately, there are a multitude of tips and solutions to remedy the situation.
From adjusting the sleeping position to the use of specific devices such as orthoses or nasal strips, the options are varied.
By addressing the root causes, such as airway obstructions or loose throat tissue, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, it is possible to significantly improve sleep quality.
What is snoring and why does it occur?
Discovering the roots of nocturnal noise.
Snoring, often the subject of jokes, is actually a warning signal about our respiratory health during sleep.
This sound phenomenon occurs when air struggles to circulate freely in the respiratory tract, causing the tissues of the pharynx to vibrate.
But what reduces this airflow?
The answer is a complex mix of personal anatomy, lifestyle habits, and sometimes, medical conditions like sleep apnea.
Anatomical structures such as the jaw, soft palateand nostrils play a crucial role, as does sleeping on the back, which increases the risk of airway obstruction.
Snorers can explore a range of remedies, from anti-snoring pillows pillows designed to encourage a lateral sleeping position, to anti-snoring devices such as mandibular advancement orthoseswhich move the jaw slightly forward to open up the airway.
Identifying and treating underlying causes , such as obstructive sleep apnea, can not only improve sleep quality but also protect against the associated cardiovascular risks.

💊Anatomy of snoring
When the respiratory tract becomes a musical instrument.
The architecture of our airways is the key to understanding snoring.
Elements such as the tonsils, uvulaand soft tissues at the back of the throat can relax during sleep, narrowing the space through which air must pass.
This restriction creates nasal congestion or upper airway obstruction, amplifying the vibrations or noise of snoring.
The use of nasal dilators or sprays can help reduce this congestion, while the use of orthoses intranasal or buccal orthoses work to prevent obstruction by holding the jaw and tongue in an optimal position, promoting smoother, quieter breathing.
💊Factors that aggravate snoring
The usual culprits behind the nocturnal symphony.
Several risk factors exacerbate snoring, turning a light rustle into a full concert.
Being overweight, for example, increases pressure on the airways, while alcohol and certain medications excessively relax the throat muscles, making obstructions easier.
Solutions such as losing weight,avoiding alcohol before bedtime, andusing ergonomic pillows to maintain a proper sleeping position can help reduce these risks.
For cases ofsleep apnea, devices such as the CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) offer a more radical solution, providing a constant flow of air to prevent pauses in breathing and significantly improve sleep quality.
How do you know why you snore?
Go from mystery to clarity with a few simple steps.
Determining the cause of your snoring is essential to finding the right remedy.
It may seem like a detective's quest, but with the right tools and a little observation, you can identify the key factors.
Start with a self-assessment, noting :
- frequency,
- the intensity of your snoring,
- and if you wake up feeling rested.
Visit sleep tracking applications can give you insights into your sleep quality and the presence of apnea.
If you have a partner, ask him or her to note whether your snoring is constant throughout the night, or if it varies.
Also take into account your lifestyle habits, such as :
- alcohol consumption,
- smoking,
- and your sleeping position.
A simple change, like sleeping on your side instead of on your back, can make a big difference.
For those who suspect more complex causes, such as sleep apnea, specific devices such as mandibular advancement orthoses or CPAP machines can be explored after medical consultation.

💊Snoring self-assessment
Be your own sleep detective.
Self-assessment is your first step towards understanding your snoring.
Use a sleep diary to document when and how you snore:
- Is it more intense after consuming alcohol or a large meal?
- Does sleeping on your side reduce the frequency of your snoring?
Tools like sleep tracking apps and recordings can help you capture patterns you might not otherwise notice.
This initial step is crucial in determining whether your snoring is simply the result of poor sleeping habits , or whether it indicates more serious sleep disorders .
💊When should you see a doctor?
Don't play doctor when your health is at stake.
If your self-assessment efforts have not borne fruit, or if you have symptoms such as :
- respiratory arrest during the night,
- excessive daytime sleepiness ,
- or if you often wake up with a headache, it's time to consult a specialist.
ENT specialists and sleep specialists can perform tests such as polysomnography to analyze your sleep in depth.
They can determine whether your snoring is related to sleep apnea or other nocturnal breathing disorders.
Don't let undiagnosed snoring disrupt your life; a visit to the doctor can put you on the road to restful sleep and quiet nights.
Non-surgical solutions to stop snoring
Explore a world of possibilities without going under the knife.
Stopping snoring does not necessarily mean resorting to surgical intervention.
There are a multitude of non-invasive options that can make all the difference.
These solutions focus mainly on lifestyle changes and theuse of anti-snoring devices designed to facilitate the passage of air and reduce, if not eliminate, the vibrations that cause snoring.
Simple adjustments to your daily routine and the introduction of certain sleep aids can help you say goodbye to noisy nights.
Lifestyle changes
Simple adjustments for peaceful nights.
Changing certain lifestyle habits can have a significant impact on your snoring.
For example, maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the airways, thus reducing the risk of snoring.
Avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime can also prevent excessive relaxation of the throat muscles.
Sleeping on your side instead of on your back prevents your tongue from blocking the passage of air.
Moisturizing and maintaining good nasal hygiene, including the use of nasal sprays or dilators, can also improve nighttime breathing.
💊Anti-snoring devices
Technology and innovation to the rescue of your nights.
On the market, a wide range of anti-snoring devices promise to provide a solution for those seeking to reduce their snoring.
One of the most promising options is the intranasal orthosis such as that offered by Back2Sleep.
This little technological marvel is designed to fit easily into the nostrils, gently widening the nasal space to facilitate airflow and reduce vibration without discomfort.
Unlike more invasive solutions, the intranasal orthosis is a discreet, comfortable and easily accessible solution, offering an effective alternative for those seeking to improve their quality of sleep without surgical intervention.
Alternative approaches to reduce snoring
Explore gentle, natural methods for a peaceful night's sleep.
Alongside medical solutions and anti-snoring devices, there are a variety of alternative approaches that can help you combat snoring without the need for surgery or invasive treatments.
These methods, which range from breathing exercises to theuse of natural remedies, offer a gentle, non-intrusive way to improve the quality of your sleep and that of your partner.
💊Exercises to reduce snoring
Tone your throat and say goodbye to snoring.
The breathing exercises and strengthening the throat muscles are an effective way of reducing snoring.
By regularly practicing exercises that specifically target the muscles involved in snoring, you can reduce the frequency and intensity of snoring.
These exercises include :
- singing techniques,
- tongue movements,
- and pronunciation exercises, which work to tone and strengthen the tissues of the throat.
By devoting a few minutes a day to these practices, you can significantly improve air circulation during sleep, reducing the vibrations that cause snoring.
💊Natural remedies and herbs
Nature to your rescue against night-time nuisance.
In addition to exercise, theuse of natural remedies and herbs can offer valuable support in the fight against snoring.
Solutions such as peppermint sprays, eucalyptus inhalations or relaxing herbal teas before bedtime can help clear the airways and promote smoother breathing.
Essential oils, whether diffused or applied topically, can also help reduce inflammation and improve nasal breathing.
These natural approaches, combined with lifestyle changes, offer a comprehensive strategy for reducing snoring and improving sleep quality.
Frequently asked questions about snoring
Q. Does everyone snore?
No, not everyone snores. Snoring affects a large proportion of the population to varying degrees, but its prevalence and intensity vary considerably from person to person
Factors such as gender, age, weight and health conditions can influence the likelihood and severity of snoring.
For example, men are statistically more likely to snore than women, and snoring can worsen with age or weight gain.
However, it's important to note that even people with none of these risk factors can experience snoring episodes under certain conditions, such as when suffering from a cold or allergies.
Q. Is snoring a sign of health problems?
Snoring can be a simple annoyance, but it can also signal underlying health problems.
In some cases, snoring is closely linked to disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea, a condition where breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep.
This association is not systematic, but loud, regular snoring, especially if accompanied by pauses in breathing, excessive daytime sleepiness or morning headaches, should prompt consultation of a health professional.
Identifying and treating these potential conditions is crucial to preventing long-term complications such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease and mood disorders.

- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.